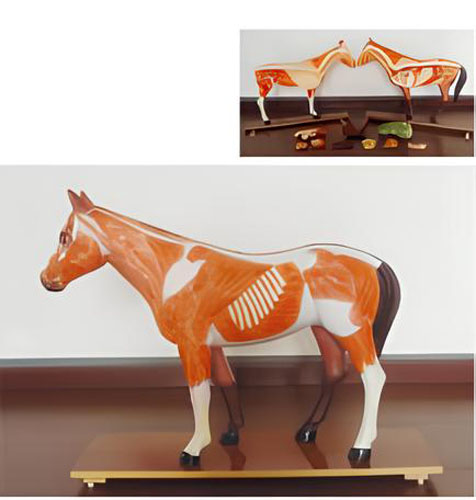
A horse's anatomy can be broken down into several key parts:
1. **Head**: The head of a horse is large and features a long snout with nostrils that open wide to help them breathe in large volumes of air. Horses have a keen sense of smell and vision, which they use for navigation and spotting predators or prey.
2. **Ears**: Horses have large, flexible ears that they can move independently to focus on specific sounds. They also have the ability to rotate their ears 180 degrees, allowing them to listen behind themselves.
3. **Neck**: The neck of a horse is long and strong, supporting its head and providing it with a good field of vision. It's covered with muscles that allow the horse to move its head and neck with great agility.
4. **Shoulder**: The shoulder of a horse is where the neck meets the body. It's an area of high muscle density, which provides strength for movement and carrying loads.
5. **Thorax (Chest)**: The chest is where the lungs are located. Horses have a large chest cavity to support their respiratory needs.
6. **Ribs**: The ribs are long and flat, providing protection for the internal organs.
7. **Back**: The back of a horse is muscular and serves as a foundation for the powerful hindquarters.
8. **Tail**: The tail serves multiple purposes including balancing while moving or standing, swatting flies, and signaling to other horses.
9. **Pelvis**: The pelvis is a strong, broad structure that supports the hindquarters and connects to the spine.
10. **Hindquarters**: This is the area that includes the hips, buttocks, and the powerful muscles used for propulsion when running.
11. **Hind Legs**: These are long and powerful, with a well-defined hock joint that allows for the rapid extension needed for galloping.
12. **Forelegs**: The forelegs are shorter than the hind legs and have a similar structure. They provide balance and support while the horse is standing or walking.
13. **Hooves**: Horses have hooves instead of claws, which helps protect their feet from the rough terrain and provides better traction.
14. **Ankle**: The ankle is not visible in horses due to the presence of a bone called the cannon bone, which extends from the knee to the fetlock joint.
 15. **Fetlock Joint**: This is the joint between the lower leg and the hoof, which allows for the horse's distinctive gait patterns.
15. **Fetlock Joint**: This is the joint between the lower leg and the hoof, which allows for the horse's distinctive gait patterns.Understanding these components helps explain how horses function, both in terms of their physical capabilities and their behavior.
Parameter:On the right side of the sagittal section, muscles are shown, and organs in the chest and abdominal cavity can be removed
Dimension: 680x200x600(mm)